Design Pharmacy Management System
Pharmacy Management System
We'll cover Following
- Introduction to the Case Study scenario.
- Identification of Entities.
- Identification of Attributes.
- Identification of Relationships.
- ER Diagram with assumptions and explanation.
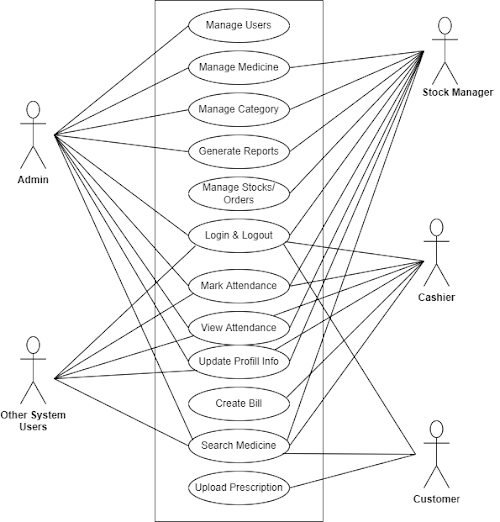
- Identification of Actors.
- Identification of Business Processes.
- Functional Requirements of the system.
- Non-Functional Requirements of the system.
- Normalization of the Relation drawn using the ER Diagram.
- Relational Database schema with foreign key references.
- SQL statements on table creation and populating them (CREATE and INSERT statements).
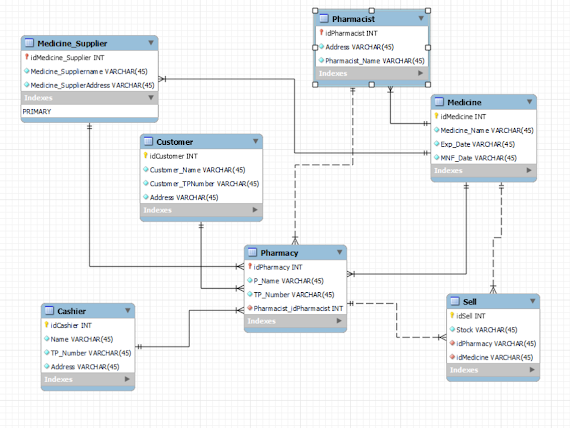
Pharmacy Management System ER Diagram
This ER (Entity Relationship) Diagram represents the model of the Pharmacy Management System Entity. The entity-relationship diagram of the Pharmacy Management System shows all the visual instruments of database tables and the relations between Medicine, Pharmacy, Cashier, Customer, Pharmacist, etc. It used structured data to define the relationships between structured data groups of Pharmacy Management System functionalities. The main entities of the Pharmacy Management System are Pharmacy, Medicine, Cashier, Customer, Pharmacist.
Pharmacy Management System entities and their attributes:
- Pharmacy Entity: Attributes of Pharmacy are pharmacy_id, TP_number, name, address
- Medicine Entity: Attributes of Medicine are name,expiry_date, manufactured_date
- Pharmacist Entity: Attributes of Pharmacist are pharmacist_id, name, address, TP_number,
- Cashier Entity: Attributes of Cashier are cashier_id, TP_number, address, name
- Customer Entity: Attributes of Customer are name, TP_number, address
- Medicine Supplier: Attributes of Medicine Supplier are address,medicine_id, name,supplier_id
- Bill Entity
- Pharmacy has a Pharmacist
- Pharmacy have medicine supplier
- Supplier supply Medicine
- Pharmacist give Medicine
- Pharmacy has Cashier
- Cashier issues Bill
- Customer sell Bill
- Pharmacy has Customer
- Pharmacy sell Medicine
- The details of Pharmacy is stored into the Pharmacy tables respective with all tables
- Each entity ( Cashier, Pharmacy, Pharmacist, Customer, Medicine, medicine supplier) contains primary keys and unique keys.
- The entity pharmacist, medicine supplier has bound with pharmacy, Medicines entities with foreign key
- All entities Pharmacy, Medicine supplier, Medicine, Pharmacist are normalized and reduce duplicity of records
- There is one-to-one and one-to-many relationships available between Pharmacy, Pharmacist, Cashier, Medicine, sell
- We have implemented indexing on each table of Pharmacy Management System tables for fast query execution.


.png)
.png)
Comments
Post a Comment